Specifications of fuel level sensor can sometimes seem confusing or overwhelming, especially, if you are unfamiliar with the terminology. In the sensor industry, manufacturers commonly state an accuracy of 99.5%, but this is sometimes misunderstood by customers.
This brief technical note will explain to help customers better understand how accuracy of sensor calculated.
1. Percent of full scale (%FS or %FSD)
The accuracy of all deflection instruments is specified by the manufacturer as a percentage of full-scale deflection (FSD).
For example, a voltmeter with an FSD of 100 V might have its accuracy stated as ±0.5%. In this case, the maximum possible error at all points on the scale is ±0.5% of 100 V or ±0.5 V. Thus when the pointer is indicating exactly at 100 V, as shown in figure 1 (a), the measured voltage is correctly stated as 100 V ±0.5 V, or 99.5 V to 100.5 V. The actual level of the measured voltage might be anywhere from 99.5 V to 100.5 V.
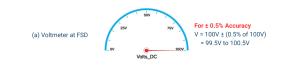
Fig.1a: Accuracy in Deflection Instruments when the Voltmeter at FSD
When the pointer of this voltmeter indicates 50 V, as illustrated in figure 1 (b), the actual measured voltage must be taken as 50 V ± (0.5% of full-scale deflection), or 50 V ± 0.5 V. This means that the measured voltage is somewhere between 49.5 V and 50.5 V. The ±0.5 V error is ±1% of 50V.
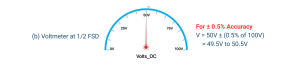
Fig.1b: Accuracy in Deflection Instruments when the Voltmeter at 1/2 FSD
When the pointer of this voltmeter indicates 25 V, as illustrated in figure 1 (c), the actual measured voltage must be taken as 25 V ± (0.5% of full-scale deflection), or 25 V ± 0.5 V. This means that the measured voltage is somewhere between 24.5 V and 25.5 V. The ±0.5 V error is ±2% of 25V.
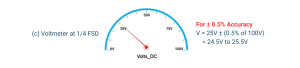
Fig.1c: Accuracy in Deflection Instruments when the Voltmeter at 1/4 FSD
If an instrument has accuracy specified as % FSD then the error will have a fixed value no matter where the pointer is in the measurement range.
2. How is the accuracy of the LIGO sensor calculated?
The accuracy of LIGO fuel level sensor is calculated base on % FSD (of the length or level). The sensors were reported to have an accuracy of 99.5%, which means an accuracy 0.5% FSD.
It should be noted that this accuracy is calculated by the manufacturer based on the length of the sensor, In some cases where customers convert the level to volume (litter), the accuracy includes both the sensor accuracy (0.5% FSD) and the calibration accuracy.
Accuracy (by volume) = 0.5 % FSD + Error during the calibration process (at customer site)
The calibration error on the customer’s side depends on the accuracy of the equipment and calibration tools, the number of steps in the calibration table, and the shape of the fuel tank. Typically, the calibration error is around 2%.
Therefore, to achieve high accuracy, customers need to carry out the calibration process carefully and precisely.
Written by Quang Nguyen, CEO